Arm Cortex Texas Instruments Jacinto/Sitara: Configuring Memory area (bus)
For SoCs (e.g. AM24xx, AM64xx, AM26xx) with multiple cores organized into clusters, you must manually select the memory area (bus) to successfully perform Debug | Download.
Possible solution
Specify Memory area (bus)
1. Open Debug | Configure Session | SoCs | Program Files | Program File.2. Select:
- Memory area (bus) associated with the core or
- Virtual Memory area (bus)
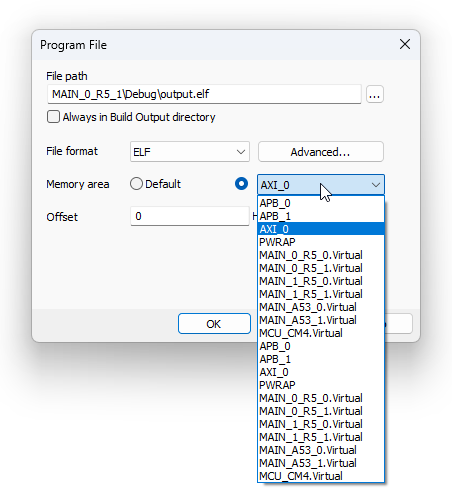
Explanation
Core clusters and bus architecture
It's common for modern embedded processors to include multiple cores organized into clusters. The cores within a cluster communicate with each other and with external peripherals through a bus architecture. For example, the CM4 core is in another cluster as the R5 core, and they are associated with different buses (e.g., AHB_1 bus for AM26xx).
Selection of a Memory area (bus) in winIDEA
With more simple SoC (with one core), winIDEA configures the Memory area (bus) for you. However, SoC with a more complicated structure of core clusters, you have to define the memory area manually.
Virtual Memory Area
Another solution is to select a Virtual Memory Area. Virtual Memory allows a process to use more memory than is physically available by using space on disk as an extension of RAM. If you select a virtual memory area through another core, winIDEA uses a mechanism where one core is involved in managing the virtual memory space for another core.
More resources in winIDEA Help
Same category topics
- RCAR-S4 configuration for Renesas evaluation board
- Arm Cortex NXP LPC1xxx: Read protection (CRP) area at 0x2FC
- Arm Cortex Texas Instruments CC2650: SWO pin configuration
- Arm Cortex Texas Instruments AWR18xx/68xx: Soft Reset
- Arm Cortex: Mismatch between Editor and Watch Window for double-float variables